Affiliate marketing is now a well-known and successful business concept for both businesses and individuals in the digital era. It is a performance-based marketing technique that enables companies to increase their customer base and revenues while giving consumers the opportunity to get money for endorsing goods or services. We will examine the principles, tactics, and major players in affiliate marketing as we delve into the deep workings of this vast manual.
1.Understanding Affiliate Marketing

A symbiotic relationship exists between the advertiser (or merchant), the affiliate (or publisher), and the customer in affiliate marketing. Let’s dissect each part to understand how it functions:
Advertiser (Merchant):
The company or business that sells goods or services is known as the advertiser. Advertisers use affiliate marketing as a low-cost method of publicising and growing their clientele. Advertisers give affiliates specific tracking links or codes so they can keep track of the leads and sales they generate.
Affiliate (Publisher):
Affiliates can be bloggers, social media influencers, website owners, or email marketers. They are self-employed marketers or content creators who promote the advertiser’s goods or services.Depending on the conditions of the affiliate programme, affiliates may receive commissions based on particular actions, such as sales, clicks, leads, or impressions.
Consumer:
The consumer, who is the end user who interacts with the affiliate’s promotional content and eventually purchases the product or performs the required action, is frequently influenced by the affiliate’s marketing initiatives, such as product reviews, suggestions, or promotional content.
2.The Affiliate Marketing Process
Several critical steps are included in the affiliate marketing process:
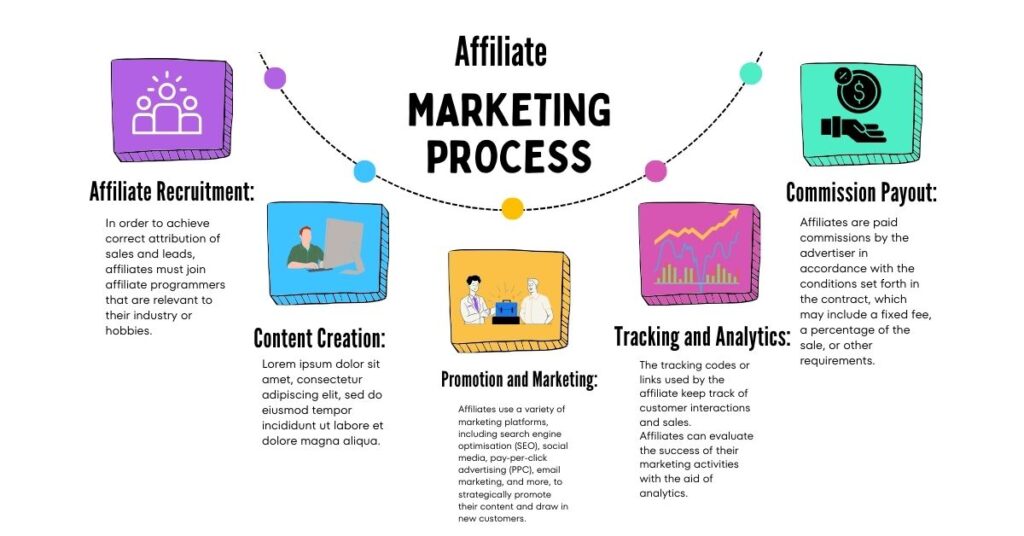
Affiliate Program Setup:
Affiliate Marketing
To attract affiliates, advertisers develop affiliate programmers, either internally or through affiliate marketing networks. These programmed include commission schemes, tracking settings, and marketing materials.
Affiliate Recruitment:
In order to achieve correct attribution of sales and leads, affiliates must join affiliate programmers that are relevant to their industry or hobbies.
Content Creation:
Affiliates produce material, such as blog entries, product reviews, social media posts, videos, email newsletters, or banner advertisements, to promote the advertiser’s goods or services.
Promotion and Marketing:
Affiliates use a variety of marketing platforms, including search engine optimisation (SEO), social media, pay-per-click advertising (PPC), email marketing, and more, to strategically promote their content and draw in new customers.
Tracking and Analytics:
• The tracking codes or links used by the affiliate keep track of customer interactions and sales.
Affiliates can evaluate the success of their marketing activities with the aid of analytics.
Consumer Engagement:
• Affiliates interact with customers by giving them useful information, responding to their questions, and gaining their confidence.
• The secret to effective affiliate marketing is for marketers to establish relationships with their customers.
Conversion:
• A conversion occurs when a user clicks on an affiliate’s tracking link and then completes the targeted activity (such as making a purchase).
• Conversions are monitored and given credit to the appropriate affiliate.
Commission Payout:
• Affiliates are paid commissions by the advertiser in accordance with the conditions set forth in the contract, which may include a fixed fee, a percentage of the sale, or other requirements.
3.Types of Affiliate Marketing

There are various affiliate marketing models, each with a special strategy and remuneration scheme:
Pay-Per-Sale (PPS):
The PPS model, which is the most popular and frequently offers greater commissions, pays affiliates a percentage of every sale made using their referral links.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC):
• Regardless of whether a transaction occurs, affiliates are paid a commission depending on the volume of clicks generated through their referral links.
• Advertisers frequently pay a set sum for each click.
Pay-Per-Lead (PPL):
• When suggested clients perform particular steps, including registering for a newsletter, completing a form, or seeking additional information, affiliates receive commissions.
PPL is frequently used in the finance and insurance sectors.
Pay-Per-Impression (PPI) or Cost-Per-Mille (CPM):
• Affiliates receive payment based on how many times their promotional content is viewed, usually per thousand views.
• Display advertising uses CPM more frequently.
Two-Tier Affiliate Marketing:
• In this business model, affiliates can find new affiliates to work with and profit from the leads or sales they bring in.
• It motivates partners to create their own affiliate networks.
4.Choosing Affiliate Programs
Success depends on choosing the correct affiliate programmes to join.
Relevance:
• Pick programmes that cater to your target market or niche. Conversion rates rise when you promote goods or services that are appropriate for your content.
Commission Structure:
• Consider the available commission rates. While some programmes may provide lower percentages and sell higher-priced goods, others may offer larger percentages and sell lower-priced goods.
Affiliate Support:
• Seek for programmes that offer marketing materials, tracking resources, and support to affiliates.
Reputation and Trustworthiness:
• Look into the credibility and reputation of the advertising. You wish to highlight goods or services provided by respectable companies.
Cookie Duration:
• After a user hits an affiliate link, the cookie duration controls how long the affiliate is given credit for a sale. Longer cookie lengths are often preferable.
Payment Methods:
• Think about the affiliate program’s payout options and regularity (such as monthly or bi-weekly).
5.Affiliate Marketing Strategies

Successful affiliate marketers use a variety of tactics to increase their profits:
Content Marketing:
• Produce useful, high-quality content that speaks to the wants and passions of your target market.
• Naturally include affiliate connections into your content..
SEO Optimization:
• To increase organic traffic, optimise your content for search engines.
• Pay attention to backlink building, on-page SEO, and keyword research.
Email Marketing:
• Create an email list and use it to send recipients specific promotional emails.
• To nurture leads and increase conversions, use email automation.
Social Media Promotion:
• Use social media to interact with your audience and share affiliate products.
• For better visibility, use hashtags, stories, and live videos.
Paid Advertising:
• Invest in paid advertising campaigns to promote your affiliate content, such Google Ads or Facebook Ads.
• Consider your alternatives for targeting and your budget.
Product Reviews:
• Create in-depth, frank product reviews that offer prospective consumers useful information.
• Incorporate affiliate links into your reviews.
Webinars and Tutorials:
• Run webinars or make instructional videos outlining the proper use of affiliate items.
• Offer insightful information that motivates viewers to act.
6. Challenges and Pitfalls

Affiliate marketing has a lot of potential, but it also has its share of difficulties and pitfalls:
Competition: Finding a distinctive viewpoint or specialty in the fiercely competitive affiliate marketing industry is crucial..
Compliance: To keep your audience’s trust, you must follow advertising standards and disclose any affiliate ties.
Algorithm Changes: Traffic and rankings may be impacted by changes to social media platforms or search engine algorithms.
Conversion Tracking: It can be difficult to ensure precise conversion tracking, and errors may occur.
Quality Over Quantity: Instead of attempting to produce large amounts of low-quality traffic, concentrate on creating great content and focused visitors.
7. Tracking and Analytics:
Using monitoring and analytics tools is necessary to monitor the success of your affiliate marketing efforts:
Google Analytics: gives information on user behavior, website traffic, and referral sources.
Affiliate Dashboards: Dashboards providing real-time information on clicks, conversions, and earnings are available through many affiliate programmed.
Link Tracking Tools: To keep track of how each affiliate link is performing, use link tracking software.
Conversion Tracking: Use conversion tracking pixels or codes to correctly attribute sales.
Conclusion

Affiliate marketing is a vibrant and lucrative sector that presents many opportunities for both organizations and individuals. You may create a prosperous affiliate marketing firm by grasping the principles, using successful techniques, and consistently adjusting to market changes. Always keep in mind that perseverance, patience, and moral behavior are necessary for long-term success in this industry. Affiliate marketing can be a wonderful method to make money and support the expansion of businesses throughout the world if done correctly and with effort.
